|
|
-
Purpose:
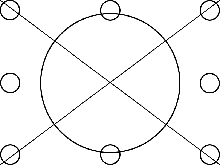
This image is to check the linearity of the display
device. That's a fancy way to say "Is the
middle of the picture in the middle of the
screen?"
-
-
What to look
for:
The center circle should be round, not egg-shaped.
The lines from corner to corner should be straight.
The small edge-locate circles along the edges are so
you can tell if you are seeing all the way to the
edge of the image. (In other words, see if the screen
is cutting of the edge of the image.)
|

|
|
|
-
Purpose:
General purpose.
-
-
What to look
for:
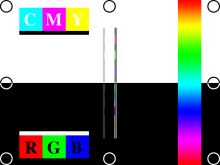
Lots of goodies here. Along the right side is a
"rainbow" with all the possible colors.
Along the sides are the edge-locate circles again.
The large color sqares in the black area are RGB pure
colors - useful to determine if a color is missing.
If there is one missing, that square will be black.
The color squares in the white are "cyan",
"magenta" and "yellow". Printers
usually use these colors rather than RGB. Then there
are the thin, vertical lines in the center. These can
be used to see if any of the colors are misaligned. A
common cause would be different length cables for at
least one of the channels.
|

|
|
|
-
Purpose:
To check black, white, and the levels of grey.
-
-
What to look
for:
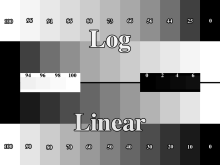
The numbers are "percent of full white".
Thus "90" means "90% of true
white" or "just a little darker than true
white". Ideal would be for you to be able to see
the difference between "0" and
"2" and see the difference between
"98" and "100". If you are
checking out a projector, you probably won't be
able to. So, use the brightness, contrast, and gamma
to change the way the image looks. On a projector,
you will probably lose a couple black squares and a
couple white squares. There is no gamma applied to
the log scale.
|
Would you like a copy of these on your computer? They are
available as: